Prepare effectively for your exams with a collection of important two-mark questions from the chapter “Electrostatics.” These concise questions cover key concepts like Coulomb’s law, electric field, potential, and capacitance. Each answer is precise and to the point, making it easier for students to revise and grasp core topics quickly. A must-have resource for scoring better in your Physics exam!
Chapter 2: Current Electricity – Important 2 Mark Questions
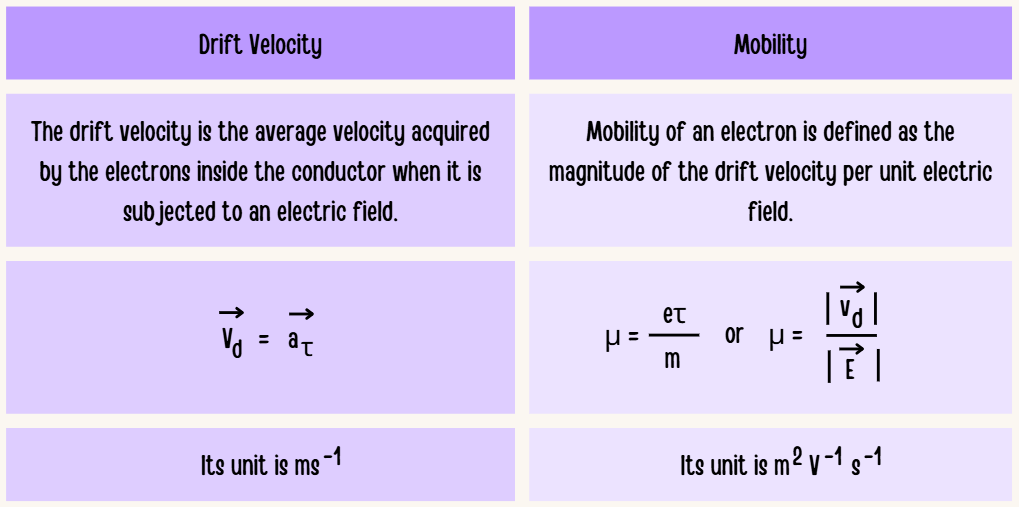
1.Distinguish between drift velocity and mobility?
2.Define Resistivity or electrical resistivity?
Electrical resistivity of a material is defined as the resistance offered to current flow by a conductor of unit length having unit area of cross section.
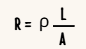
Its unit is ohm-metre Ωm
3.State kirchoff’s voltage rule?
It states that in a closed circuit the algebraic sum of the products of the current and resistance of each part of the circuit is equal to the total emf included the circuit.
This rule follows from the law of conservation of energy for an isolated system.
4.State Kirchoff’s Current rule?
Kirchhoff’s current rule states that the algebraic sum of the currents at any junction of a circuit is zero. It is a statement of law of conservation of electric charge.
5.State microscopic form of ohm’s law?
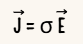
- J is the current density,
- E is the Electric Field,
- σ is the conductivity.
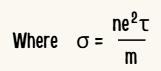
6.State macroscopic form of ohm’s law?
Macroscopic form of Ohm’s law can be stated as “the potential difference across a given conductor is directly proportional to the current passing throught it when the temperature remains constant”.
V = IR
7.What is peltier effect?
When an electric current is passed through a circuit of a thermocouple, heat is evolved at one junction and absorbed at the other junction. This is known as peltier effect.
8.State joule’s law of heating
It states that the heat developed in an electrical circuit due to the flow of current varies directly as
- H = I2RT
- The square of the current
- The resistance of the circuit and
- The time of flow.
9.What is Seebeck effect?
Seebeck discovered that in a closed circuit consisting of two dissimilar metals, when the junctions are maintained at different temperatures an emf (potential difference) is developed. The current that flows due to the emf developed is called thermoelectric current.
10.Why current is a scalar?
Current has both magnitude and direction. But the direction of current does not obey vector laws of addition. So, current is a scalar quantity.
11.Define temperature coefficient of resistance?
It is defined as the ratio of increase in resistivity per degree rise in temperature to its resistivity at T
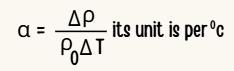
Two Mark Questions
Volume 1
- 1.Electrostatics
- 2.Current Electricity
- 3.Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
- 4.Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
- 5.Electromagnetic waves
Volume 2
