12th Physics | Chapter 9 | Important 2 Mark Questions | Atomic and Nuclear physics
Important two-mark questions from the chapter “Atomic and Nuclear Physics” are provided to aid in exam preparation. Topics such as Bohr’s model, atomic spectra, radioactivity, and nuclear reactions are covered. These answers are designed to ensure clarity and support effective revision for scoring high marks!
1.What is isotope?Give example?
isotopes are atoms of the same element having same atomic number Z, but different mass number A.
For example, hydrogen has three isotopes and they are represented as
- 1 1H (hydrogen),
- 21H (deuterium),and
- 31H (tritium).
2.What is isotone? Give an example?
Isotones are the atoms of different elements having same number of neutrons. 512B and 613C are examples of isotones with 7 neutrons each.
3.write the properties of cathode rays?
- Cathode rays possess energy and momentum and travel in a straight line with high speed of the order of 107 ms-1.
- It can be deflected by application of electric and magnetic fields.
- The direction of deflection indicates that they contain negatively charged particles.
- When the cathode rays are allowed to fall on matter, heat is produced.
- Cathode rays affect the photographic plates and also produce fluorescence when they fall on certain crystals and minerals.
- When the cathode rays fall on a material of high atomic weight, x-rays are produced.
- Cathode rays ionize the gas through which they pass.
- The speed of cathode rays is up to
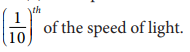
4.What is meant by excitation energy?
The energy required to excite an electron from lower energy state to any higher energy state is known as excitation energy.
5.Define – curie?
- One curie was defined as number of decays per second in 1 g of radium and it is equal to 3.7×1010 . decays/s.
- 1 Curie =1 Ci = 3.7×1010 × decays/s. per second
- 1 Ci = 3.7×1010 Bq
6.What is meant by activity or decay rate? Give its unit?
activity (R) or decay rate which is the number of nuclei decayed per second and it is denoted as
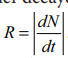
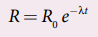
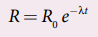
- The SI unit of activity R is Becquerel
- There is also another standard unit for the activity called Curie(Ci).
- 1 Curie =1 Ci = 3.7×1010 × decays/s. per second
- 1 Ci = 3.7×1010 Bq
7.What are the constituent particles of Neutron and Proton?
According to quark model, proton is made up of two up quarks and one down quark and neutron is made up of one up quark and two down quarks
8.State the properties of neutrino.
Properties of neutrino:
- It has zero charge;
- It has an antiparticle called anti-neutrino.
- Recent experiments showed that the neutrino has very tiny mass.
- It interacts very weakly with the matter. Therefore, it is very difficult to detect.
9.Define radioactivity?
The phenomenon of spontaneous emission of highly penetrating radiations such as α, β and γ rays by an element is called radioactivity and the substances which emit these radiations are called radioactive elements.
10.Define ionization potential?
- Ionization potential is defined as ionization energy per unit charge.
- Thus, for a hydrogen atom (Z=1), the ionization potential is
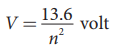
11.Define impact parameter?
The impact parameter is defined as the perpendicular distance between the centre of the gold nucleus and the direction of velocity vector of alpha particle when it is at a large distance.
12.What is radio carbon dating?
- Using this technique, the age of an ancient object can be calculated.
- by using radio carbon isotope (14C)
Two Mark Questions
Volume 1
- 1.Electrostatics
- 2.Current Electricity
- 3.Magnetism and magnetic effects of electric current
- 4.Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current
- 5.Electromagnetic waves
Volume 2
